Write route handlers
How could a web framework without programming ability be called framework? By the end of this tutorial, you'll learn how to write route handlers and return different kind of responses to the frontend.
Create a project
Let's create a new project for programming code.
cargo init hello-teo-handlers --bin
cd hello-teo-handlersReplace the file content of Cargo.toml with this.
[package]
name = "hello-teo-handlers"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
[dependencies]
teo = { version = "0.3.9" }
tokio = { version = "1.0", features = ["full"] }Replace the file content of src/main.rs with this.
use tokio::main;
use teo::prelude::{App, Result};
#[main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let app = App::new()?;
app.run().await
}Now we've just created a barebone Teo server app. Don't forget to create a schema
file like before. Create a file named schema.teo in the root directory of the
project with the following content.
server {
bind: ("0.0.0.0", 5051)
}
request middlewares [logRequest]Run this command to start our server:
cargo run -- serveThis time we're not using Teo CLI because we want our custom code to be loaded and
compiled. Now a barebone server is started with every routes lead to NotFound error
with 404 code.
Most of the times, the routes that we write are for API interactions. Frontend clients request these APIs for structured data. JSON is the most popular data format. Depending on business needs, some API routes return HTML documents, images and files. These routes are not designed for frontend clients to intercharge data with. And the response values are not structured data like JSON. Teo will not include these routes in the generated frontend clients. That is, the routes that we write fall into two main categories: API interaction and Non-API interaction.
Non-API interaction
HTML response
Let's begin with create a home page for this server.
Append this to the end of schema.teo.
@map(.get, "/")
declare nonapi handler hello(): AnyReplace the content with src/main.rs with this.
use tokio::main;
use teo::prelude::{App, Response, Result, Error};
#[main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let app = App::new()?;
app.main_namespace().define_handler("hello", || async {
let response = Response::html(r#"
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello, Teo handlers</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, Teo handlers!</h1>
</body>
</html>
"#)?;
Ok(response)
});
app.run().await
}With this updated code, we define a handler named "hello" to match what
we've declared in our schema. Stop the running server process and restart the server.
Navigate to "http://localhost:5051" in a browser, you will see the
new home page that we've just write in HTML.
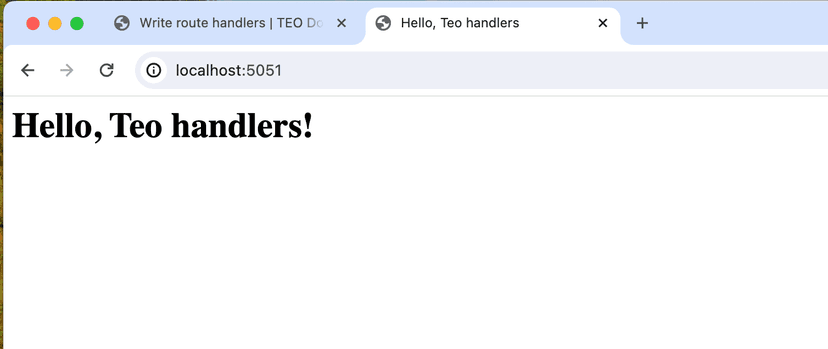
In practice, any template engines can be used to generate the HTML content. But it's far beyond this scope.
Empty response
Let's have a rest and write something simple.
Add these to the schema and the source code file.
@map(.get, "/empty")
declare nonapi handler empty(): Anyapp.main_namespace().define_handler("empty", || async {
Ok(Response::empty())
});Restart our server and request to /empty.
curl http://localhost:5051/emptyThe output is blank since this is an empty response.
Text response
Let's write a text response which echos user's url segment input.
Add these to our schema.
entity {
provider: .rust,
dest: "./src/entities"
}
@map(.get, "/echo/:data", interface: "EchoPathArguments")
declare nonapi handler echo(): AnyRun this command to generate interfaces.
cargo teo generate entityReplace src/main.rs with the following content.
mod entities;
use tokio::main;
use teo::prelude::{App, Response, Result, Error};
use crate::entities::EchoPathArguments;
#[main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let app = App::new()?;
app.main_namespace().define_handler("hello", || async {
let response = Response::html(r#"
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello, Teo handlers</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, Teo handlers!</h1>
</body>
</html>
"#)?;
Ok(response)
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("empty", || async {
Ok(Response::empty())
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("echo", |path_args: EchoPathArguments| async move {
Ok(Response::string(path_args.data()?, "text/plain"))
});
app.run().await
}We've included the generated path arguments into our code and use it in our handler.
Start our server again.
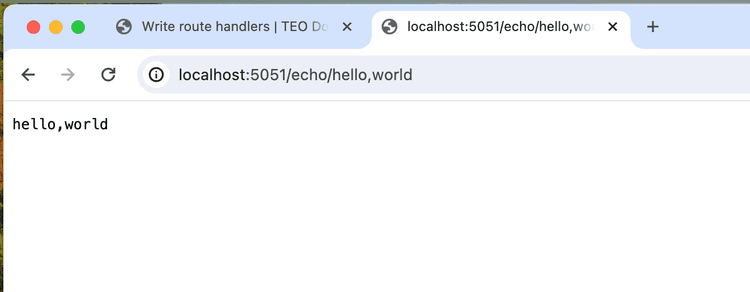
cargo run -- serveNow navigate to /echo/hello in the browser. The path argument is printed out.
File response
Let's server some static files from a directory.
Create a file at /static/images/girl.webp with the following image.

Append this to the end of the schema.
@map(.get, "/static/*path", interface: "StaticPathArguments")
declare nonapi handler static(): AnyRepeat the code generation process.
cargo teo generate entityUpdate src/main.rs to this.
mod entities;
use tokio::main;
use teo::prelude::{App, Response, Result, Error};
use crate::entities::{EchoPathArguments, StaticPathArguments};
#[main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let app = App::new()?;
app.main_namespace().define_handler("hello", || async {
let response = Response::html(r#"
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello, Teo handlers</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, Teo handlers!</h1>
</body>
</html>
"#)?;
Ok(response)
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("empty", || async {
Ok(Response::empty())
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("echo", |path_args: EchoPathArguments| async move {
Ok(Response::string(path_args.data()?, "text/plain"))
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("static", |path_args: StaticPathArguments| async move {
Response::send_file("static", path_args.path()?)
});
app.run().await
}Start the server again.
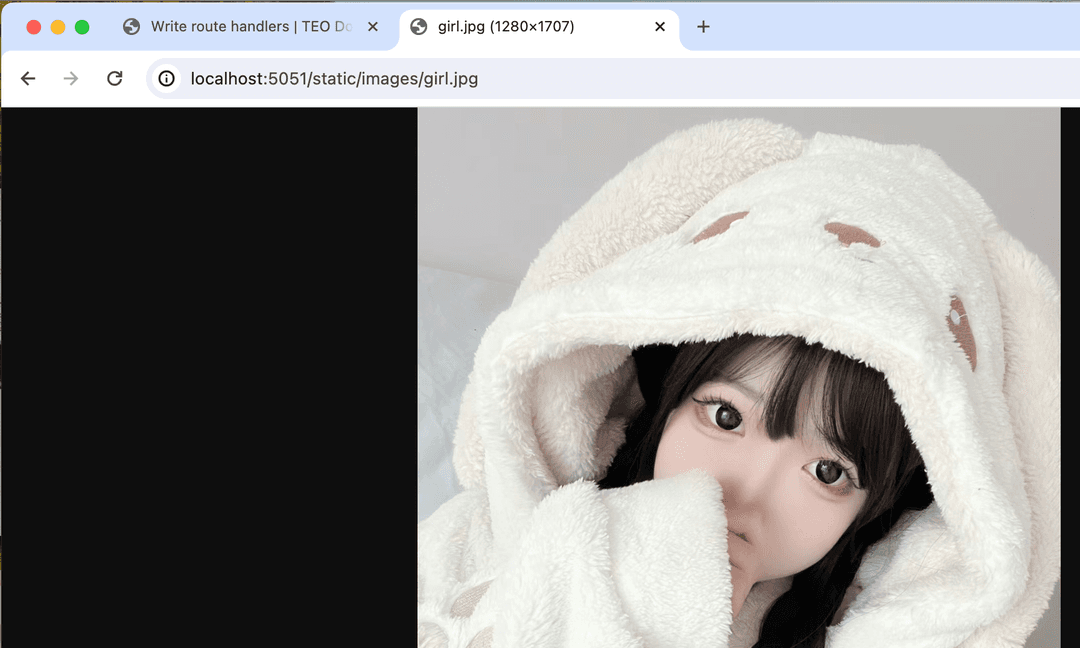
cargo run -- serveNow navigate to /static/images/girl.webp in the browser, and you will see the
image. Try typing a non-existing file path, 404 is responded.
API interaction
JSON is the only response data format that Teo supports. If you have requirements for other data types. Let us know by firing an issue.
JSON request
Let's add some models and perform some model updates from JSON requests.
Replace schema.teo with this.
server {
bind: ("0.0.0.0", 5051)
}
request middlewares [logRequest]
connector {
provider: .sqlite,
url: "sqlite::memory:"
}
entity {
provider: .rust,
dest: "./src/entities"
}
@map(.get, "/")
declare nonapi handler hello(): Any
@map(.get, "/empty")
declare nonapi handler empty(): Any
@map(.get, "/echo/:data", interface: "EchoPathArguments")
declare nonapi handler echo(): Any
@map(.get, "/static/*path", interface: "StaticPathArguments")
declare nonapi handler static(): Any
interface AlterCreatedAtInput {
id: Int
createdAt: DateTime
}
model Record {
@id @autoIncrement @readonly
id: Int
value: Int?
@onSave($when(.create, $now)) @readonly
createdAt: DateTime
@onSave($now) @readonly
updatedAt: DateTime
declare handler alterCreatedAt(AlterCreatedAtInput): Data<Result<Record>>
}Generate the entities again.
cargo teo generate entityThen replace src/main.rs with this.
mod entities;
use tokio::main;
use teo::prelude::{App, Response, Result, Error, teon};
use crate::entities::{AlterCreatedAtInput, AlterCreatedAtInputTrait, EchoPathArguments, StaticPathArguments, Teo};
#[main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let app = App::new()?;
app.main_namespace().define_handler("hello", || async {
let response = Response::html(r#"
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello, Teo handlers</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, Teo handlers!</h1>
</body>
</html>
"#)?;
Ok(response)
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("empty", || async {
Ok(Response::empty())
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("echo", |path_args: EchoPathArguments| async move {
Ok(Response::string(path_args.data()?, "text/plain"))
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("static", |path_args: StaticPathArguments| async move {
Response::send_file("static", path_args.path()?)
});
app.main_namespace().define_model_handler_group("Record", |group| {
group.define_handler("alterCreatedAt", |teo: Teo, input: AlterCreatedAtInput| async move {
if let Some(record) = teo.record().find_unique_object(teon!({
"where": {
"id": input.id()
}
})).await? {
record.set_created_at(*input.created_at())?;
record.save().await?;
Ok(Response::data(record.to_teon().await?))
} else {
Err(Error::not_found())?
}
});
});
app.run().await
}This way, Teo becames a normal ORM and developers can write any code to
interact data with. The createdAt field is readonly, but through custom
handlers, it becomes modifiable.
Form request
Let's try some file uploading. Upload an image to the static directory that we've created before.
Append this to the schema.
@map(path: "/upload")
declare form handler upload(UploadInput): Data<UploadOutput>
interface UploadInput {
file: File
}
interface UploadOutput {
path: String
}Generate interfaces.
cargo teo generate entityUpdate src/main.rs to be like this.
mod entities;
use std::path::PathBuf;
use std::time::{SystemTime, UNIX_EPOCH};
use tokio::main;
use teo::prelude::{App, Response, Result, Error, teon};
use crate::entities::{AlterCreatedAtInput, AlterCreatedAtInputTrait, EchoPathArguments, StaticPathArguments, Teo, UploadInput, UploadInputTrait};
#[main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let app = App::new()?;
app.main_namespace().define_handler("hello", || async {
let response = Response::html(r#"
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello, Teo handlers</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, Teo handlers!</h1>
</body>
</html>
"#)?;
Ok(response)
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("empty", || async {
Ok(Response::empty())
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("echo", |path_args: EchoPathArguments| async move {
Ok(Response::string(path_args.data()?, "text/plain"))
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("static", |path_args: StaticPathArguments| async move {
Response::send_file("static", path_args.path()?)
});
app.main_namespace().define_model_handler_group("Record", |group| {
group.define_handler("alterCreatedAt", |teo: Teo, input: AlterCreatedAtInput| async move {
if let Some(record) = teo.record().find_unique_object(teon!({
"where": {
"id": input.id()
}
})).await? {
record.set_created_at(*input.created_at())?;
record.save().await?;
Ok(Response::data(record.to_teon().await?))
} else {
Err(Error::not_found())?
}
});
});
app.main_namespace().define_handler("upload", |input: UploadInput| async move {
let original_location = PathBuf::from(input.file().filepath.as_str());
let extension = if let Some(ext) = original_location.extension() {
".".to_owned() + ext.to_str().unwrap()
} else {
"".to_owned()
};
let nanos = SystemTime::now().duration_since(UNIX_EPOCH).unwrap().subsec_nanos();
let random_file_name = nanos.to_string();
let destination_string = format!("static/images/{}{}", random_file_name, extension);
let destination = PathBuf::from(destination_string.as_str());
let path = "/".to_owned() + destination_string.as_str();
match std::fs::rename(original_location, destination) {
Ok(_) => {
Ok(Response::data(teon!({
"path": path
})))
},
Err(err) => {
Err(Error::internal_server_error_message(err.to_string()))
}
}
});
app.run().await
}Start our server again.
cargo run -- serveNow send a form request to /upload. And access the URL of the uploaded file.
The uploaded file starts downloading.
Summary
Teo is a great web framework for modeling data and writing route handlers. No matter which programming language is used, Teo try it best to be type safe and reduce duplications. This tutorial is much harder than the previous one. If you have any problems or find bugs with it, let us know by joining our Discord group or firing an issue.